TOP Malware. In this second issue of our Anida Latam Cybersecurity Newsletter, we wanted to share with you the main vulnerabilities affecting the technological environments of private and public sector organizations in recent times.
TOP Malware Series: RedLine Stealer
It is a Trojan-type malware (RAT) that operates through the "Malware-as-a-Service" (MaaS) modality. A malware designed to be marketed as a service, allowing those interested in acquiring RedLine to have a large number of actions within a compromised computer.
The business of acquiring a license to use RedLine is done through two channels on Telegram, where you can request support, product information and access to make the corresponding payment.
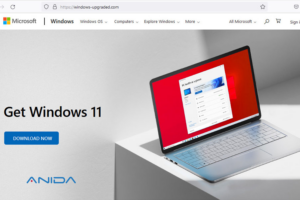
RedLine infiltrates a workstation via the Internet in order to fraudulently obtain the victim's confidential information, as well as his or her website login name, password or credit card number.
Fraudulent website to distribute RedLine as an "upgrade" to Windows 11
Ransomware on Judiciary Branch PCs "cryptolocker".
The Judicial Branch in Chile issued a computer alert due to a ransomware attack on its network and asked officials not to open or read emails or messages "of dubious origin". The attack kept the systems with serious problems, so that some scheduled hearings were suspended. They were attacked by a ransomware that adds the extension " cryptolocker" to the encrypted files.
CryptoLocker is a recent family of ransomware whose business model is based on extorting the user by kidnapping files and demanding a ransom for them (with a time limit to recover them).
It is important to note that it is generally not recommended to make the requested payments, as this does not ensure that the hijacked equipment will be returned, nor the integrity of the affected data.
CryptoLocker uses social engineering techniques to get the user to execute it. Specifically, the victim receives an email, pretending to come from a logistics company, with a ZIP file with a password attached. When the user opens it by entering the password that comes in the email, he thinks that there is a PDF file inside and when he opens it he executes the Trojan. CryptoLocker takes advantage of the Windows policy of hiding extensions by default, so that the user is tricked "thanks" to this Windows feature.
The first thing the Trojan does once it is executed on the victim's computer is to obtain the public key (PK) of a C&C server. In order to connect to its server, the Trojan incorporates an algorithm known as Mersenne twister to generate random domain names (DGA). This algorithm uses the date of the day as a seed and can generate up to 1000 different domains each day, of a fixed length.
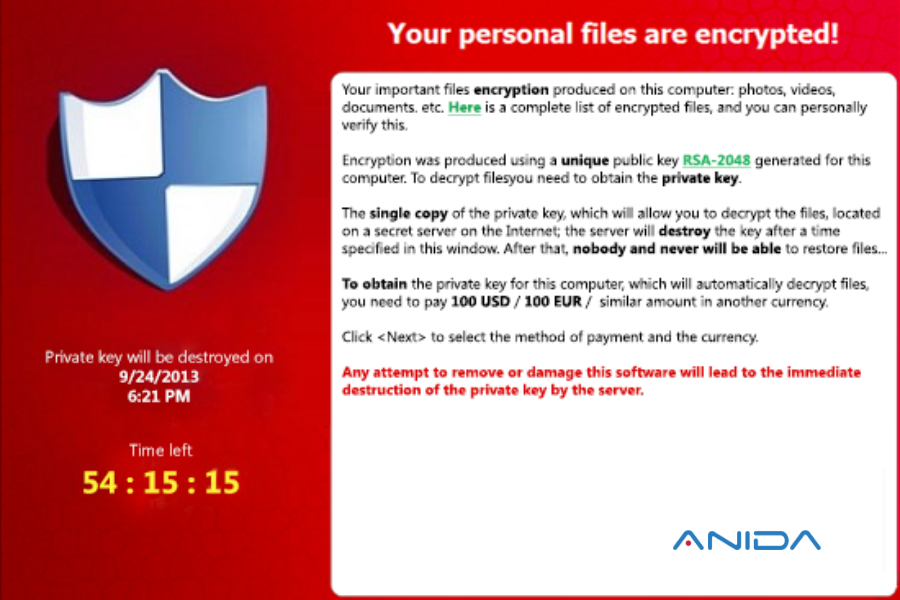
When the Trojan has finished encrypting all the files within its reach, it displays the following message asking for the ransom, giving a maximum time to pay before destroying the private key held by the author.
We will continue to report on vulnerabilities affecting the technological environments of private and public sector organizations in the next issue of this newsletter.
TOP Malware
TOP Malware
The rapid development of intelligent automation is ushering in a new era of business productivity and innovation.
Growing interest in Artificial Intelligence and application modernization is driving up spending on cloud services